HTML Beautifier vs HTML Minifier: When to Use Each Tool (Complete Guide for 2025)
HTML Beautifier vs HTML Minifier: When to Use Each Tool (Complete Guide for 2025)
In the rapidly evolving landscape of web development, developers face constant pressure to balance two seemingly contradictory goals: writing clean, maintainable code and delivering lightning-fast websites. HTML beautifiers and minifiers represent the two sides of this equation, serving distinct yet equally important purposes in modern web development workflows. Understanding when and how to use each tool can dramatically improve your development process, team collaboration, and website performance.
Understanding the Core Differences
HTML beautifiers and HTML minifiers operate as opposing forces in the code formatting spectrum, each addressing different needs within the development lifecycle. An HTML beautifier takes compressed, messy, or poorly formatted code and transforms it into a clean, well-structured format with proper indentation, spacing, and line breaks. This process makes code readable and accessible to human developers who need to understand, modify, or debug it. Beautifiers add whitespace, organize nested elements logically, and ensure consistent formatting throughout the document.
In contrast, HTML minifiers remove all unnecessary characters from code without changing its functionality. This includes eliminating whitespace, line breaks, comments, and sometimes even shortening attribute names or removing optional tags. The minified output appears as a compressed, single-line block of code that's difficult for humans to read but significantly smaller in file size. Modern minifiers can reduce HTML file sizes by 20-40% on average, with some complex documents seeing even greater reductions.
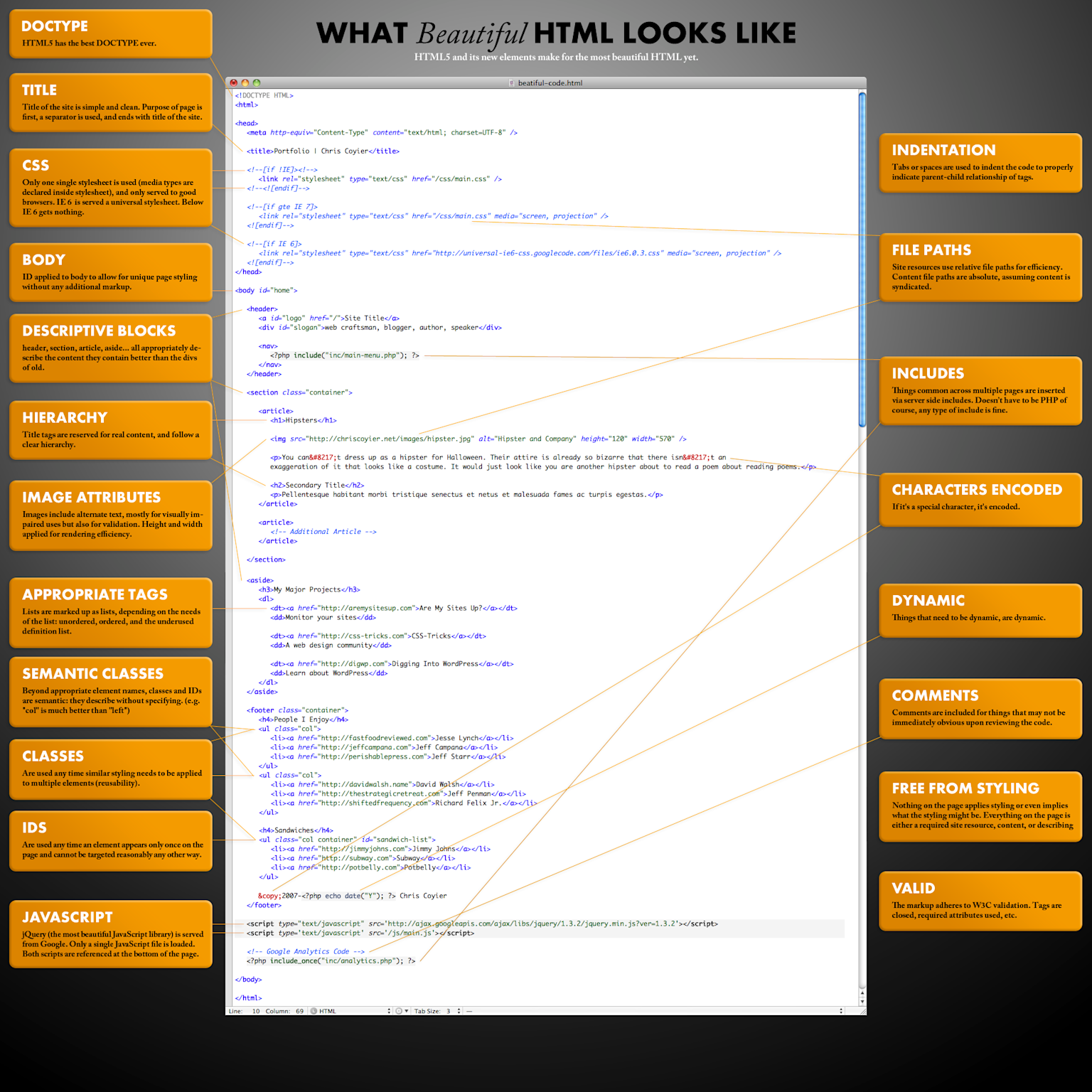
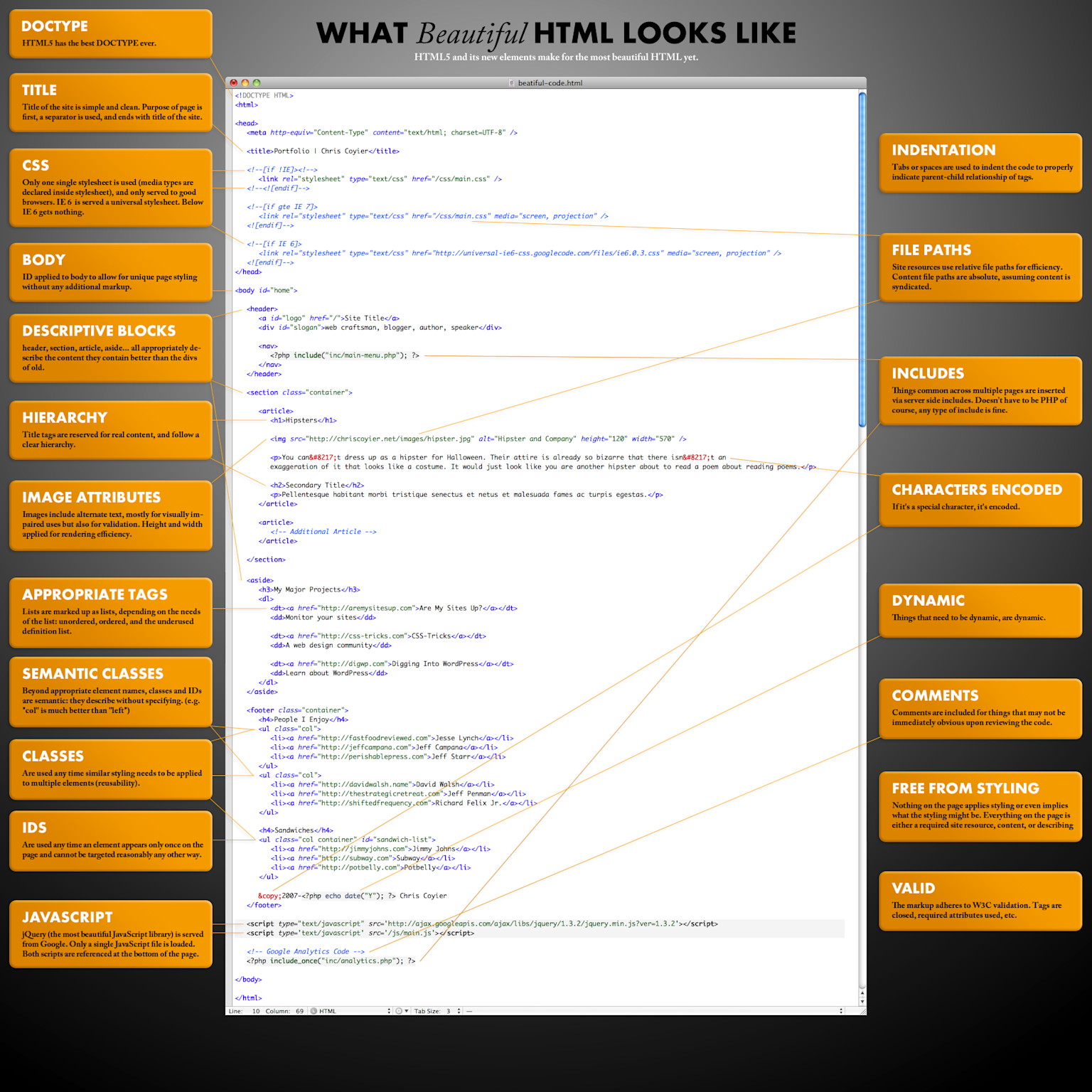
Annotated example of beautiful, well-structured HTML code showing best practices for clean, readable markup.
The philosophical difference extends beyond mere formatting. Beautifiers prioritize developer experience and code maintainability, recognizing that software is read far more often than it's written. Studies show that developers spend approximately 60% of their time reading and understanding existing code versus writing new code. Clean, well-formatted HTML accelerates comprehension, reduces cognitive load, and minimizes the likelihood of introducing bugs during modifications.
Minifiers, conversely, prioritize end-user experience through performance optimization. With Google's Core Web Vitals now directly impacting search rankings and conversion rates dropping by an average of 4.42% for every additional second of load time between 0-5 seconds, file size reduction has become critical for business success. Smaller HTML files load faster, consume less bandwidth, and improve metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Time to Interactive (TTI).
When to Use HTML Beautifiers: Development and Debugging Scenarios
HTML beautifiers excel in development environments where code readability and maintainability take precedence over file size. During active development, you and your team need to quickly understand code structure, identify nested elements, and locate specific sections for modification. Beautified code with proper indentation creates visual hierarchy that mirrors the DOM structure, making it instantly apparent which elements are children of which parents.
Code review processes benefit immensely from beautified HTML. When team members review pull requests or merge requests, consistently formatted code eliminates style debates and allows reviewers to focus on logic, structure, and potential issues. Without proper formatting, reviewers waste mental energy parsing poorly structured code before they can even begin evaluating functionality. Many organizations enforce beautification through pre-commit hooks or continuous integration pipelines to ensure all code entering the repository meets formatting standards.
Debugging and troubleshooting become significantly easier with beautified code. When investigating production issues or attempting to understand why a particular element isn't rendering correctly, developers need to quickly locate relevant HTML sections and understand the relationship between elements. Minified code obscures these relationships, turning what should be a straightforward investigation into a frustrating archaeology expedition through compressed gibberish.
Learning and onboarding represent another critical use case for beautifiers. Junior developers or team members new to a project need readable code to understand patterns, conventions, and architectural decisions. Exposing new developers to minified code during their learning phase hampers comprehension and can instill poor coding habits. Beautified code serves as both documentation and teaching tool, demonstrating best practices through example.
Working with third-party code or legacy systems often requires beautification as a first step. When you inherit a project with poorly formatted HTML or need to understand how a third-party library structures its output, running the code through a beautifier provides immediate clarity. Tools like Prettier, Code Beautify, and HTML Tidy can transform cryptic HTML into readable format within seconds, allowing you to quickly assess quality and identify potential issues.
When to Use HTML Minifiers: Production and Performance Optimization
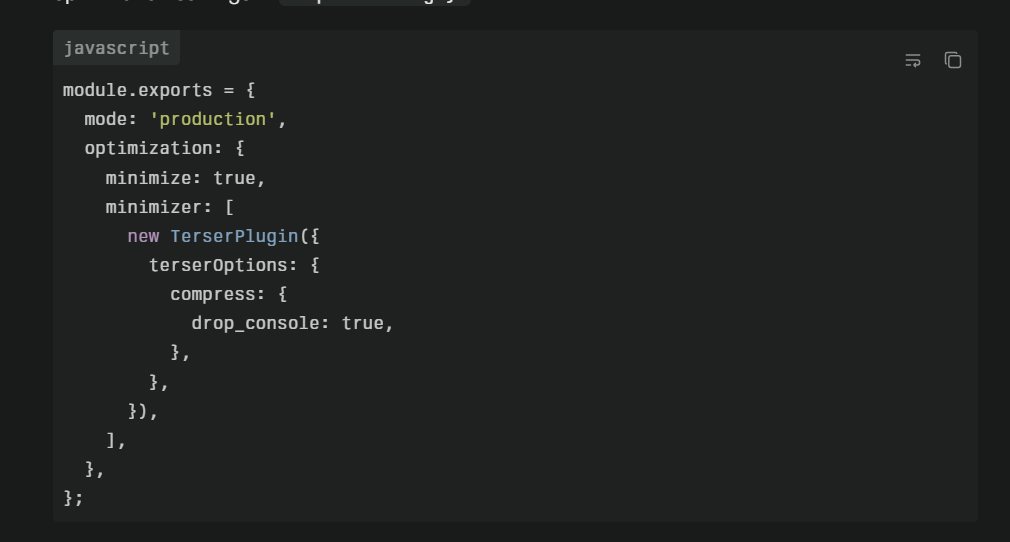
HTML minifiers become essential when preparing code for production deployment. Once development and testing conclude, minification should occur as part of your build process, creating optimized versions of your HTML files that deliver faster to end users. Modern build tools like Webpack, Vite, and Parcel include minification steps by default, recognizing its importance in production pipelines.
Performance-critical applications require minification to meet user expectations and business requirements. E-commerce sites, where every millisecond of load time impacts conversion rates, cannot afford to serve bloated HTML. Studies by Amazon found that every 100ms of latency cost them 1% in sales. For major retailers processing billions in annual revenue, those milliseconds translate to millions of dollars. Minification provides one of the easiest wins in performance optimization, requiring minimal effort for measurable gains.
Mobile optimization makes minification particularly crucial. Mobile users often access websites over cellular networks with limited bandwidth and data caps. Serving minified HTML reduces data consumption, loads pages faster on slower connections, and improves the mobile user experience. With mobile traffic now accounting for over 60% of global web traffic, optimizing for mobile devices is no longer optional.
SEO benefits emerge from minification's performance improvements. Google's algorithm now explicitly considers page speed as a ranking factor, with Core Web Vitals directly impacting search positions. Faster-loading pages rank higher, receive more organic traffic, and provide better user experiences. While minification alone won't catapult you to the top of search results, it contributes to the cumulative performance improvements that do make a difference.
Cost reduction through bandwidth savings represents a tangible benefit for high-traffic websites. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and hosting providers typically charge based on data transfer. By reducing HTML file sizes through minification, you decrease bandwidth costs proportionally. For websites serving millions of requests daily, these savings accumulate significantly over time.
Development vs Production: The Workflow Integration
The most effective approach separates development and production workflows, using beautifiers during development and minifiers for production. This separation allows developers to work with readable code while ensuring optimal performance for end users. Modern development practices embrace this dual-workflow approach through automated build processes.
During development, configure your code editor to automatically beautify HTML on save. Popular editors like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom support this through extensions like Beautify, Prettier, or HTML Formatter. Automatic beautification ensures code remains consistently formatted throughout development without requiring manual intervention, saving time and maintaining standards effortlessly.
Version control systems should store beautified, unminified code. This practice ensures that diffs are meaningful, code reviews are productive, and team members can understand changes at a glance. Attempting to commit minified code creates massive, incomprehensible diffs that obscure actual changes and make code review impossible. Your repository should contain human-readable source code, with minification occurring only during the build process.
Build pipelines automate the transition from development to production. When code moves from development through staging to production, the build process automatically minifies HTML as part of the deployment workflow. This automation eliminates human error, ensures consistency, and allows developers to focus on writing code rather than remembering to minify files manually. Tools like Grunt, Gulp, and npm scripts facilitate this automation.
Source maps bridge the gap between minified production code and readable source code during debugging. When production issues arise, source maps allow you to view the original, beautified code in browser developer tools even though minified code is actually running. This capability provides the best of both worlds: optimal production performance with maintainable debugging experience.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
Deploying beautified code to production represents one of the most common mistakes. Developers focused on functionality sometimes forget the performance implications of serving uncompressed HTML. While beautified code functions identically to minified code, it wastes bandwidth, slows page loads, and provides worse user experience. Always minify production code.
Minifying during development creates the opposite problem. Some developers, eager to optimize everything, minify their code prematurely. This practice makes development painful, debugging nearly impossible, and collaboration frustrating. Development environments should prioritize readability over file size.
Committing minified code to version control pollutes repositories with massive, incomprehensible diffs. When minified files change, the entire minified output appears as deleted and re-added in diffs, making it impossible to identify actual changes. Version control systems should store source code, not compiled output.
Mixing formatted and unformatted code within the same project creates inconsistency and confusion. When some files are beautified while others remain messy, developers waste time adjusting to different formatting styles and may introduce errors when modifying unfamiliar files. Establish project-wide formatting standards and enforce them consistently.
Over-configuring beautifiers leads to endless style debates that waste development time. The purpose of beautification is creating consistent, readable code—not achieving perfection according to individual preferences. Choose reasonable defaults (like 2 or 4 space indentation) and stick with them rather than debating minutiae.
Forgetting to test after minification can introduce subtle bugs. While rare, aggressive minification sometimes breaks JavaScript or removes critical whitespace in specific edge cases. Always test your site after the minification process to ensure functionality remains intact. Automated testing should run against minified code before production deployment.
Not using automated tools forces manual minification, which is error-prone and inefficient. Developers who manually minify code waste time and inevitably forget steps or make mistakes. Automation through build tools ensures consistency, saves time, and eliminates human error.
Tool Selection and Configuration
Prettier has emerged as the most popular beautifier for modern web development projects. Its opinionated approach eliminates configuration debates by enforcing a consistent style with minimal options. Prettier supports HTML, CSS, JavaScript, TypeScript, and numerous other formats, making it ideal for full-stack projects. Its aggressive formatting rewrites code from scratch according to its rules, ensuring absolute consistency across all files.
HTML Tidy, developed by the W3C, represents the traditional approach to HTML beautification. This command-line tool not only formats code but also fixes markup errors and upgrades legacy code to modern standards. HTML Tidy excels when working with older codebases or inherited projects that contain outdated HTML constructs requiring modernization.
Code Beautify and FreeFormatter provide browser-based beautification for quick formatting needs. These online tools require no installation and work across all platforms, making them ideal for quick tasks or situations where you cannot install local tools. Simply paste your HTML, click format, and copy the beautified output.
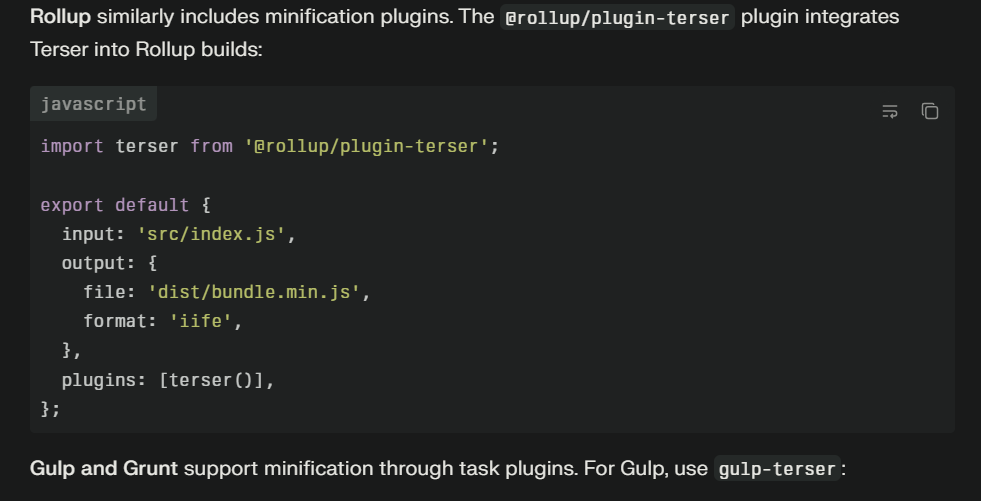
UglifyJS and Terser dominate JavaScript minification but often handle HTML within broader build processes. These tools integrate seamlessly with bundlers like Webpack and Rollup, minifying all assets—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—as part of a unified build pipeline.
HTMLMinifier provides dedicated HTML minification with extensive configuration options. This tool allows fine-grained control over what gets removed, from simple whitespace to optional tags and attribute values. Configuration options let you balance aggressiveness with safety, ensuring minification doesn't break functionality.
Google Closure Compiler offers advanced minification for large-scale projects. While more complex to configure, Closure Compiler provides the most aggressive compression with sophisticated optimization techniques. Projects handling millions of requests daily benefit from Closure Compiler's extreme optimization.
Best Practices for 2025
Automate everything through build tools and editor configurations. Manual processes fail eventually—automation ensures consistency. Configure your editor to beautify on save during development, and configure your build pipeline to minify for production. This automation removes decision fatigue and ensures best practices are followed automatically.
Establish team conventions early in projects. Agree on indentation style (tabs vs spaces), line length limits, and formatting preferences before writing code. Document these conventions and enforce them through tooling rather than code review comments. Consistency matters more than any specific style choice.
Use pre-commit hooks to enforce formatting standards. Tools like Husky and lint-staged automatically format code before commits, preventing improperly formatted code from entering version control. This automated enforcement eliminates formatting issues from code reviews, allowing reviewers to focus on logic and functionality.
Monitor performance metrics to quantify minification benefits. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and WebPageTest to measure the impact of minification on load times, Core Web Vitals, and overall performance. These measurements justify optimization efforts and identify opportunities for further improvement.
Keep source and build separate in your project structure. Store beautified source files in a src directory and output minified files to a dist or build directory. This separation makes clear which files are human-edited source code versus generated output.
Document your build process so team members understand how source code becomes production assets. Clear documentation prevents confusion and ensures everyone can reproduce the build process locally. Include information about which tools minify code and how to debug production issues using source maps.
Update tools regularly to benefit from performance improvements and bug fixes. Beautifiers and minifiers continuously improve, and staying current ensures you leverage the latest optimizations and features. However, test updates in development before pushing to production to avoid unexpected breaking changes.
The choice between HTML beautifiers and minifiers isn't either/or—it's both, applied appropriately. Beautifiers optimize for developer productivity and code maintainability during development. Minifiers optimize for user experience and performance in production. Understanding when to use each tool, and integrating both into your workflow through automation, represents best practice for modern web development in 2025.